Overview of European Geography Standards
SS6G7 Locate selected features of Europe.
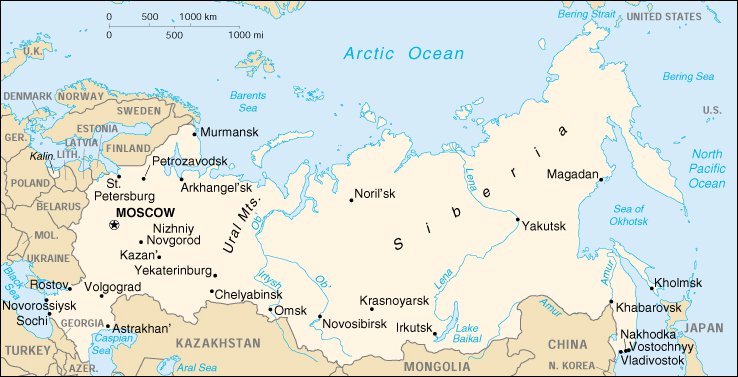
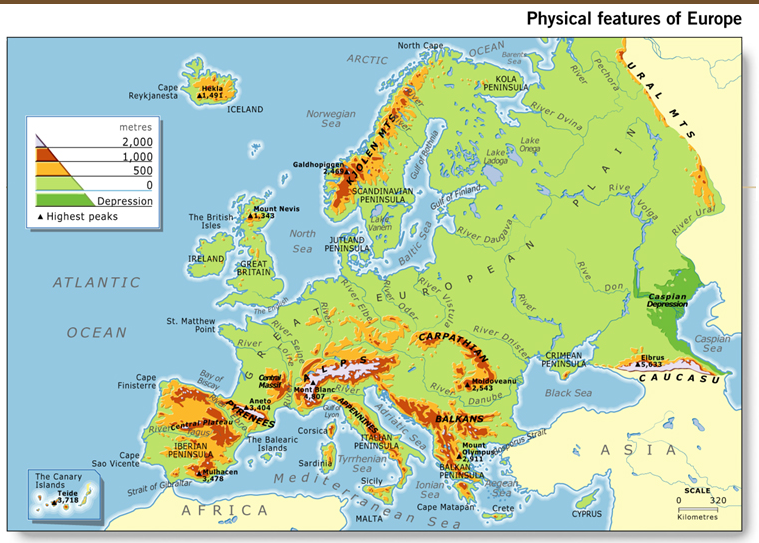
a. Locate on a world and regional political- physical map: the Danube River, Rhine River, English Channel, Mediterranean Sea, European Plain, the Alps, Pyrenees, Ural Mountains, and Iberian Peninsula.
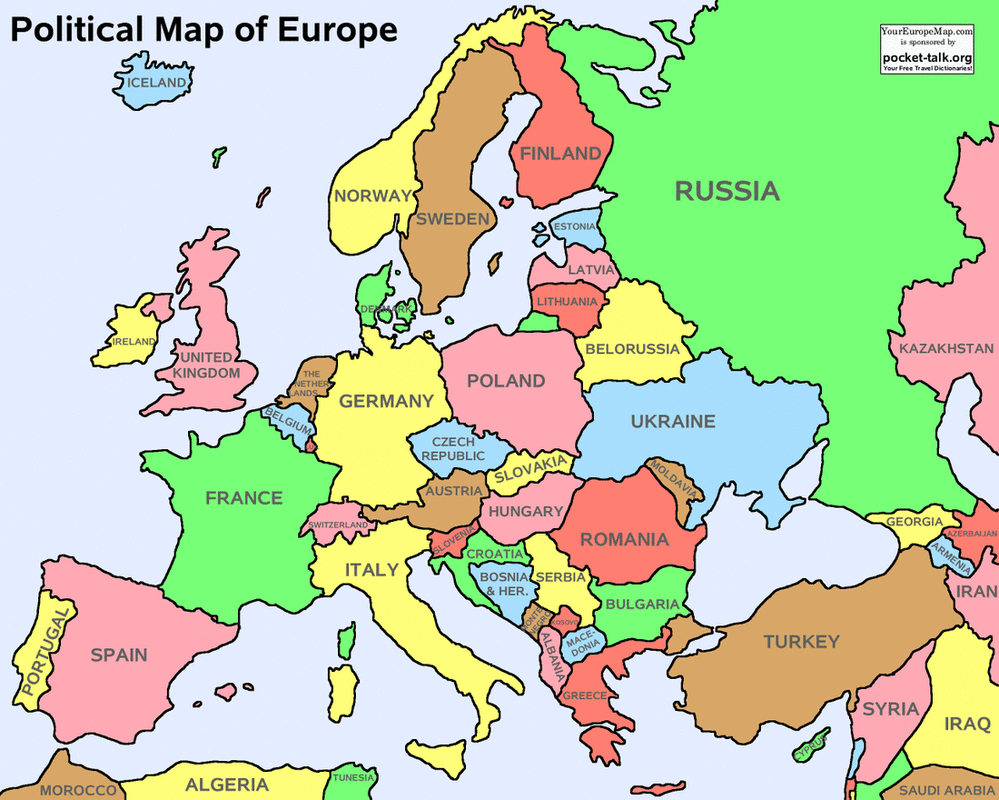
b. Locate on a world and regional political-physical map the countries of France, Germany, Italy, Russia, Spain, Ukraine, and United Kingdom.
SS6G8 Explain environmental issues in Europe.
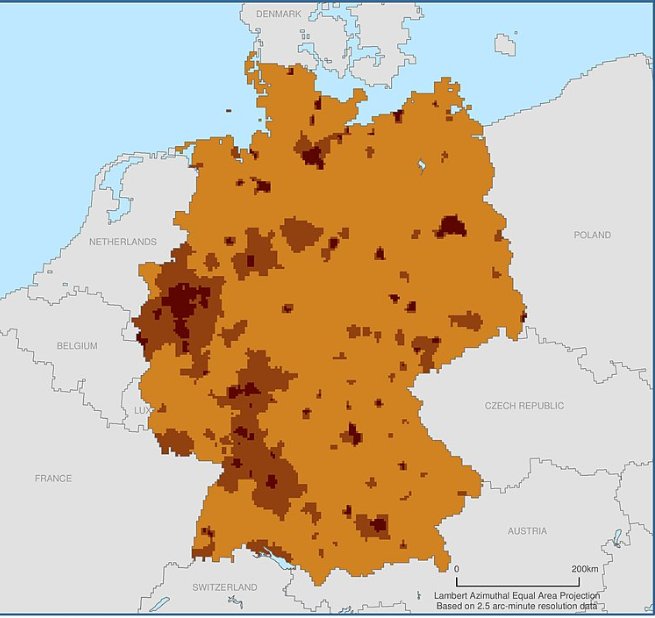
a. Explain the causes and effects of acid rain in Germany
b. Explain the causes and effects of air pollution in the United Kingdom
c. Explain the causes and effects of the nuclear disaster in Chernobyl, Ukraine.
Ukraine Nuclear Disaster
‘Voices From Chernobyl’: Survivors’ Stories
Nuclear Disaster in Ukraine (reading)
Acid Rain in Germany
Acid Rain in Germany (reading)
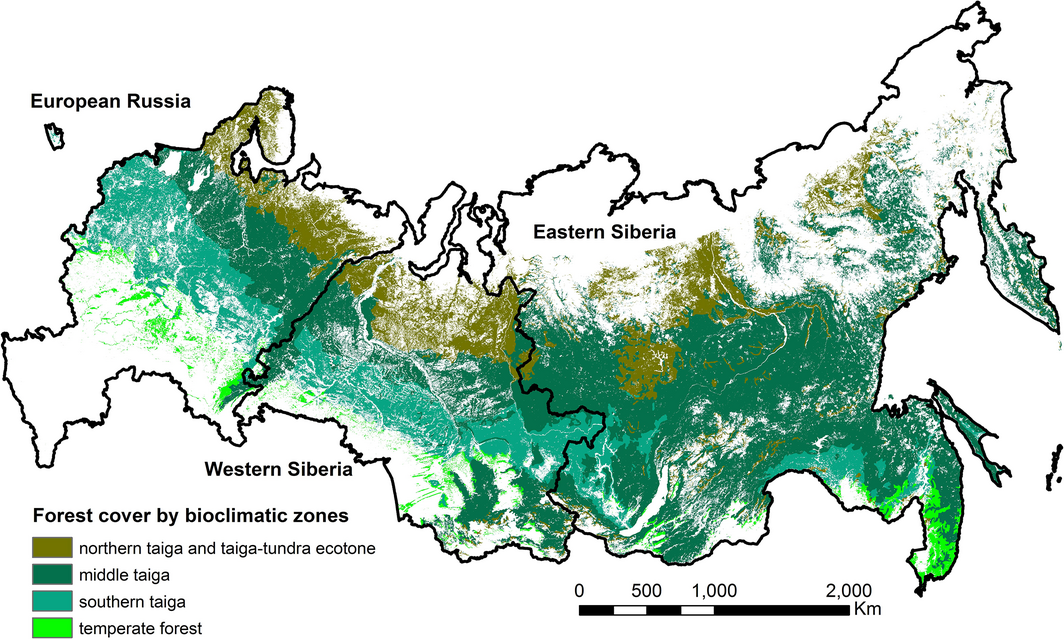
European Forests Fight for Survival
Air Pollution in the United Kingdom
Air Pollution- National Geographic
UK air pollution ‘linked to 40,000 early deaths a year!
SS6G9 Explain the impact of location, climate, natural resources, and population distribution on Europe.
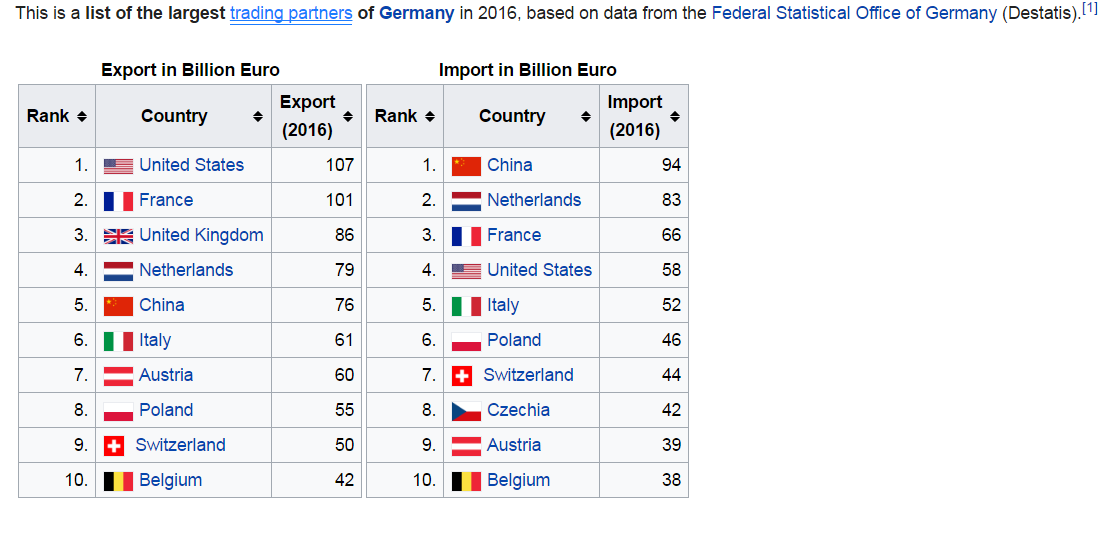
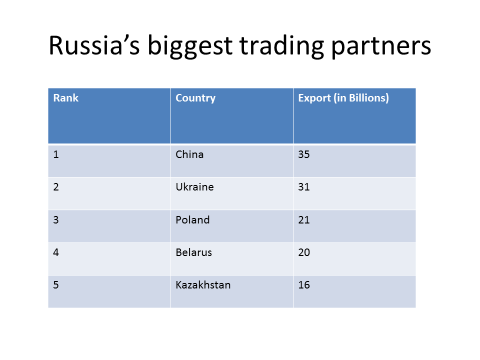
a.Compare how the location, climate, and natural resources of Germany, the United Kingdom and Russia impact trade and affect where people live.
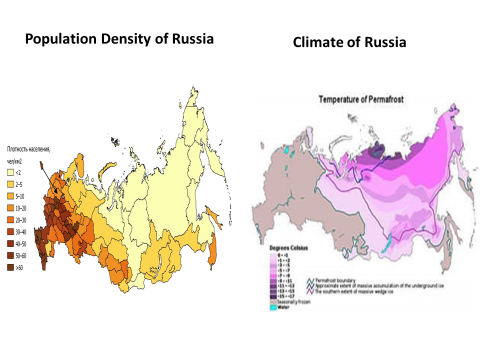
Population density and population distribution is not random! The characteristics of the location, climate, and natural resources that are present or absent in a place have a lot to do with how many people live there and what parts of the country/ area that they are most attracted to. These are called push factors and Pull Factors!
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom boasts Europe’s 3rd largest population and economy, but ranks 11th in terms of total land area. London, the capital of the U.K., is the nation’s largest population center.
Population: 65.64 Million people
Land Area: 93,628 Sq mi
Population Density: approximately 690 people per sq mi
Population Distribution: All of the UK is densely populated. There are some areas of southern and central UK where the Density is especially high.
Location
The United Kingdom is located off the coast of Western Europe, directly across the English Channel from France.
Location Pull Factors:
- United Kingdom is centrally located between many possible trade partners.
- As an Island, the UK has coastlineon all sides of the country. It has access to the North Sea to the East, the Atlantic Ocean to the West, and the English Channel to the South.
- UK’s coastlines have a high impact on population and trade
- There are many ports surrounding the United Kingdom which are used to trade.
- UK’s many ports have a high impact on population and trade
- These factors together, give the UK access extensive trade routes (and access to trade partners) used to trade around the world
- UK’s easy access to trade partners has a high impact on trade and population
Location Push Factors
- There are no large mountain ranges that would negatively impact population or trade
Climate
The climate of the U.K., which is heavily influenced by ocean currents, is relatively mild. The climate type is called temperate maritime. The nation receives frequent rainfall throughout the year, which, along with its abundant arable land, makes much of the U.K. suitable for farming and livestock grazing.
Climate Pull Factors:
- United Kingdom has a mild climatewhich doesn’t get much lower than 32° F in the winter or much higher than 90° F in the summer
- The UK’s mild climate has a relatively high impact on population and trade
- United Kingdom gets enoughprecipitation for farming at about 33.7 inches annually
- The UK’s precipitation has ahigh impact on population and trade
Climate Push Factors
- The United Kingdom does not have any extreme climate factors that would negatively impact population or trade
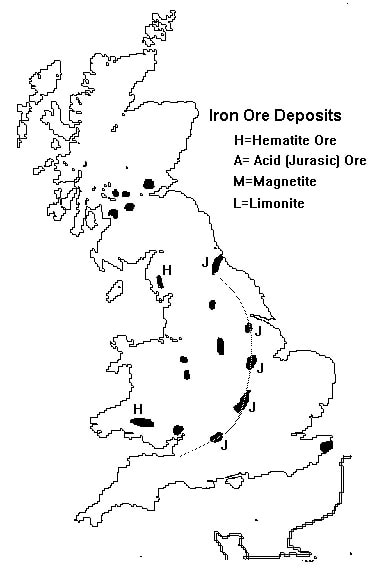
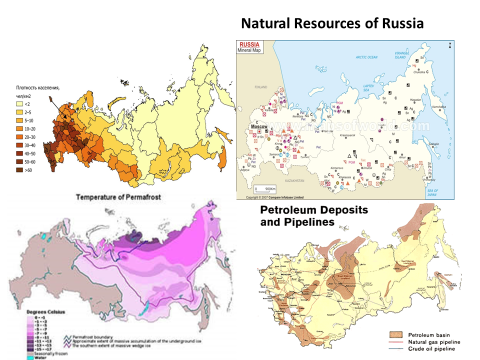
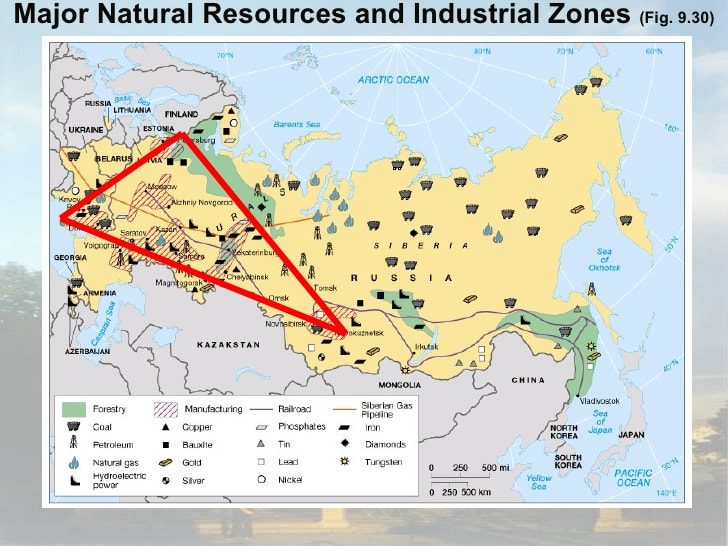
The U.K. has large deposits of coal, iron ore, natural gas, and petroleum. The country’s population centers are found in its urban areas where mining and service jobs are prevalent.Natural Resources Pull Factors
- The UK’s biggest industries areAuto production, steel manufacturing, and ship building. The country has coal fields, and deposits of iron ore, natural gas, and petroleum are used in theseindustries.
- The fact that the United Kingdom has the natural resources that are used in their biggest industries has ahigh impact on population and trade.
- Fishing is profitable and popular along the coastlines of the UK
- The fishing near the coasts has a high impact on population and trade
- 25% of the land is arable (can be farmed)
- Arable land has a high impact on population and trade.
Natural Resources Push Factors
- The UK’s coal fields were overusedand the country and now the coal deposits are almost gone.
- The depleted coal fields has alow impact on population
- The UK has used alternative sources of fuel so the depleted coal fields has had a relatively low impact on trade.
Germany
|
Location
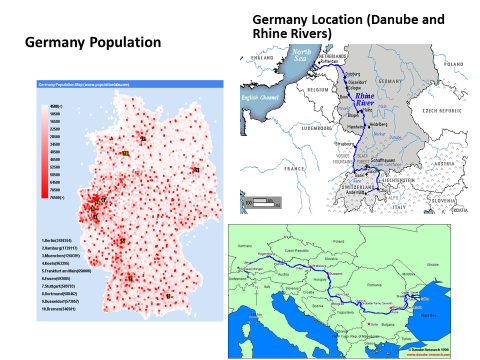
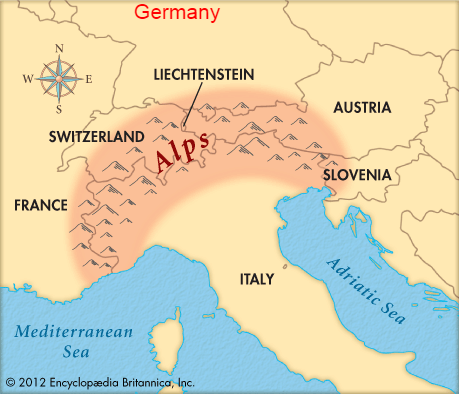
Germany is bordered to the north by Denmark, to the west by the Netherlands, Belgium, and France, to the south by Switzerland and Austria, and to the east by the Czech Republic and Poland. Most of Germany’s population centers are found in its urban areas, many of which are located in western Germany near the Rhine River; the Rhine plays a major role in transporting goods and people across the country.Location Pull Factors
Location Push Factor
|
|
Climate
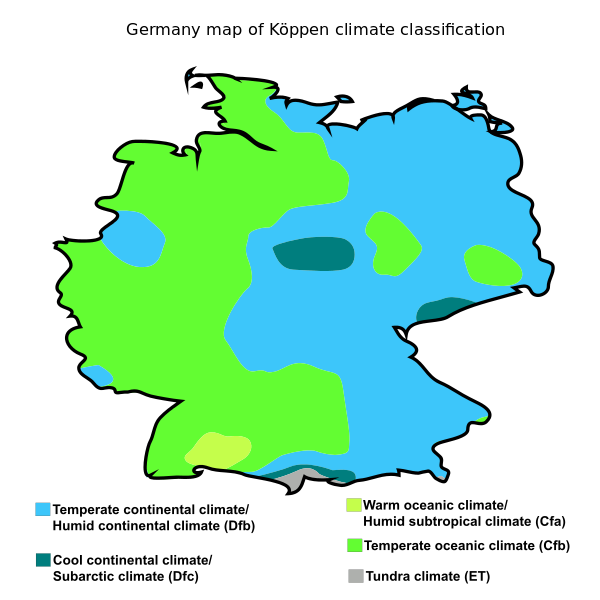
The climate of western Germany is warmer in the summer months with mild winters, while eastern Germany tends to have much colder winters and longer, hotter summers. Northwestern and coastal Germany have a maritime influenced climate which is characterized by warm summers and mild cloudy winters. Farther inland, the climate is continental marked by greater seasonal variations in temperature, with warmer summers and colder winters. In Southern Germany, near the Alps, there is a Mountain Climate which is characterized by lower temperatures and snow. Climate Pull Factors:
Climate Push Factors:
|
Here is more information about Germany’s climate: Here is more information about Maritime and Continental Climates: Here is more information about Continental Climates: Here is more information about Mountain Climates: |
|
Natural Resources
Germany has ample arable land and many lush forests supporting an abundant timber industry. The nation also has large deposits of coal and iron ore, which support two of its largest industries: the automotive and energy industries.Natural Resource Pull Factors:
|
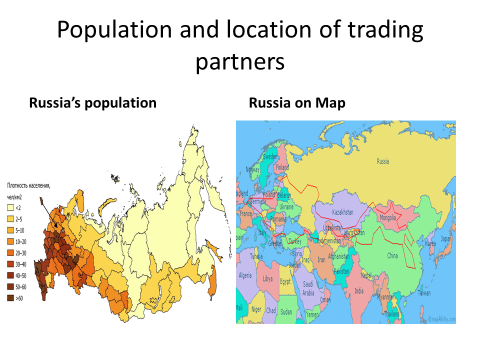
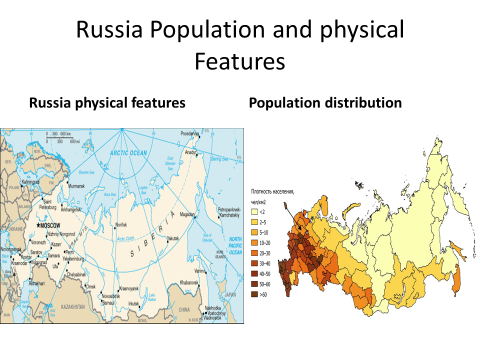
Russia is located across two continents. The majority of its land area is found in northern Asia; however, nearly a quarter of the country is located west of the Ural Mountains in Europe. Even though much of Russia is on the continent of Asia, it is still considered to be a European country because a majority of its population are closer to Europeans ethnically, culturally, and linguistically. This western portion of Russia accounts for 77% of the nation’s total population, and Russia itself has Europe’s largest total land area and population. Its economy ranks 4th in Europe. Russia’s capital, Moscow, boasts its largest population center.
|
Location
The European side of Russia is bordered to the west by Finland, Estonia, Latvia, Belarus, and Ukraine, while on the Asian side, it is bordered by Kazakhstan, Georgia, Mongolia, China, and North Korea. Russia’s Northern Coastline touches the Arctic Ocean, while its Eastern Coast is on the Atlantic Ocean.Location Pull Factors
Location Push Factors
|
|
Climate
Russia’s western climate varies between cool summers and harsh winters. In fact much of northern Russia’s soil is permanently frozen throughout the year, a phenomenon known as permafrost. Most Russians live on the European side of Russia where the climate is comparatively more hospitable.Climate Pull Factors
|
Here is more information on Permafrost: www.nationalgeographic.org/encyclopedia/permafrost/ Here is more information on Russia’s climate: www.weatheronline.co.uk/reports/climate/Russia.htm Here is more info on Russia & its climate: kids.nationalgeographic.com/explore/countries/russia/#russia-st-basils.jpg |
|
Natural Resources
Russia has vast timber resources, and a bustling mining industry in the Ural Mountains where gold, iron ore, coal, and aluminum are present. Russia also has oil and natural gas in abundance in its northern regions, particularly on the Asian side of the country, although the cold climate in this area makes their extraction difficult. Russia’s largest industries are: logging, mining, Airplane building, defense (building weapons), Agriculture &(farming),Natural Resources Pull Factors
|